
Learning how to effectively use and integrate Weaviate Cloud (WCD) queries into your iOS or macOS applications can be challenging. This article simplifies the process by focusing on the various types of queries available and providing a live tool for you to run them. We’ll offer a detailed explanation of common and easily implemented query types, and you can see the results in real-time. Additionally, Mac users can download our custom application to run live examples directly on their laptops, allowing them to copy and paste these queries as templates for their own projects.
The content is based on Adam Chan's Book Recommendation project found at this Git repo here.
Searching a Vector Database
Imagine you have a giant library with books described by numbers instead of words. A vector similarity search is like a special tool that helps you find books similar to the one you're holding by comparing their numbers. It's faster than reading every book description and works well for things like finding similar images or recommending products.
Let's say you're in the library and love a particular mystery novel. This book can be represented by a vector, a fancy way of saying it's a bunch of numbers that capture information about the book. These numbers might encode things like genre, character count, or how many times certain words appear.
Now, you want to find other similar mystery novels. The library (or the Weaviate platform in this case) uses the same kind of number code (vector) for all the books. The search tool then compares the vector of your favorite book to all the others. Books with similar vectors, meaning their numbers are close together, are likely similar mystery novels you might enjoy. This way, you can find new reads without sifting through every single book description.
Application Overview
Included is a downloadable application for Mac users to run live query examples directly on their laptop.
Feel free to copy and paste these queries into your own projects for use as a template for your own queries.
Query App: A working MacOS app that runs queries.
Query Examples: Query prompt examples.
Read more on how to use Weaviate for IOS and Mac Developers.
To get familiar with the data used and how the Weaviate Database was created, you can reference this project.
Query Helper Application
An application you can use to perform a live test of Weaviate Queries.
The MacOS app is signed by Apple and can be downloaded here.
API Settings
The first order of business is to create the API keys needed to run the application as needed.
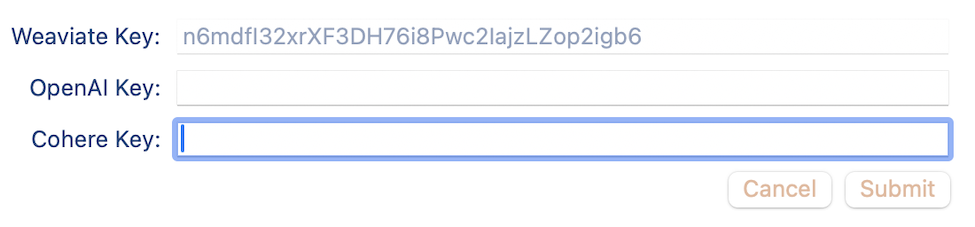
API Key Settings Panel
Of the 3 API Keys, the Weaviate API key is already defined for you and cannot be changed for this demo app.
An explanation of each key, how it is used, and a link to how to define your own appears below.
- Weaviate API Key: Access key to the Weaviate Vector DB that holds the domain data
- OpenAI API Key: Access key to OpenAI that Weaviate uses to access OpenAI Large Language Models to query embeddings. Create a key at: https://openai.com
- Cohere API Key: Access key to Cohere that Weaviate uses for text embedding, generative AI and reranking. Create a key at: https://cohere.com
Keys can be defined to the application by clicking on the settings icon to bring up the API Key Settings Panel.
Query Prompt Buttons

Query Prompt Features include:
- Copy Prompt: For use in your own apps.
- Reset Prompt to the Original One Selected: Reset, if prompt was changed
manually.
- Search Prompt: Begin Search using prompt.
Query Prompt
The Query Prompt can be changed manually in the query text box and run against a Weaviate Vector DB giving you the opportunity to experiment with your own ideas.
Query Menu
Preset query templates are accessed through the Query Menu by selecting the button of your choice.

Query Prompt Examples
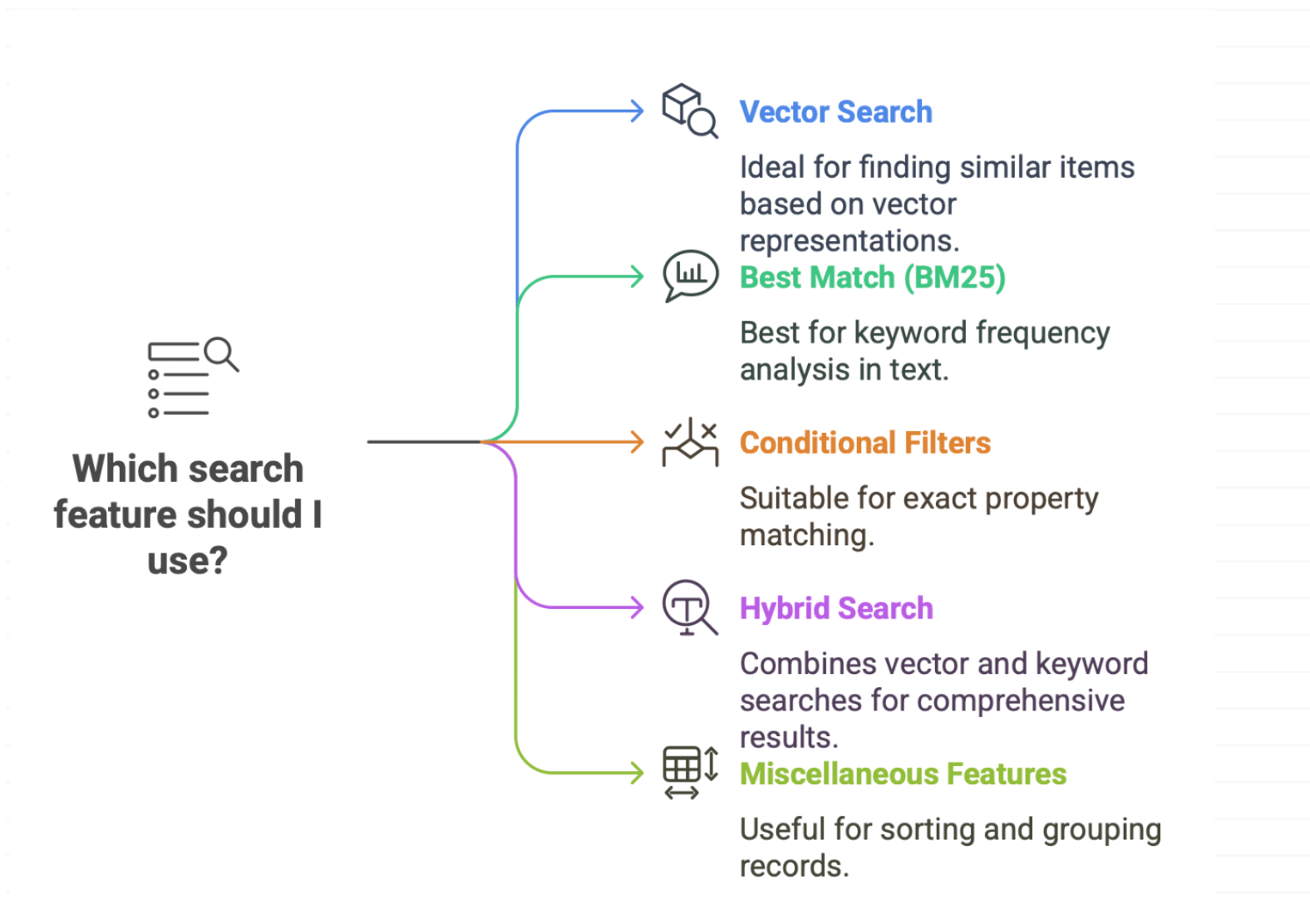
This article discusses several types of queries, all of which require a Weaviate API key. Depending on the specific query type being executed, an additional OpenAI and/or Cohere API key may also be necessary. While the required Weaviate API key is already provided, users should be aware that further API keys may be needed for certain operations.
Primary: Fundamental options for querying data.
- Basic: A simple query that retrieves a limited amount of items
- Third Item: Skip to the third item of a query
- Meta Data: Properties (eg. ID, creation date, last update date, etc) available that go beyond the original values loaded on to the vector database
Reorder: Rearranging or prioritizing the data.
- Move Away: Allow users to prioritize similar terms/concepts and deemphasize others. (+Open AI Key)
- ReRank: Change the order in which data elements are displayed, perhaps based on specific criteria. (+Open AI Key, Cohere Key)
Aggregate: Summarizing count data.
- By Category: Group counts based on specific attributes.
- Grand Total: Total count of the entire dataset.
Single Result: RAG processing resulting in a single result.
- Summary: Summary of a specific query. (+Open AI Key, Cohere Key)
- Translate To: Translate data elements or results into different languages. (+Open AI Key, Cohere Key)
- Translate From/To: Translate data elements or results from different languages to different languages. (+Open AI Key, Cohere Key)
Grouped Result: Grouping or organizing data using RAG
- Grouped Result: Perform prompt on all records retrieved from another prompt. (+Open AI Key, Cohere Key)
Primary
Basic
The basic building block for creating a query.
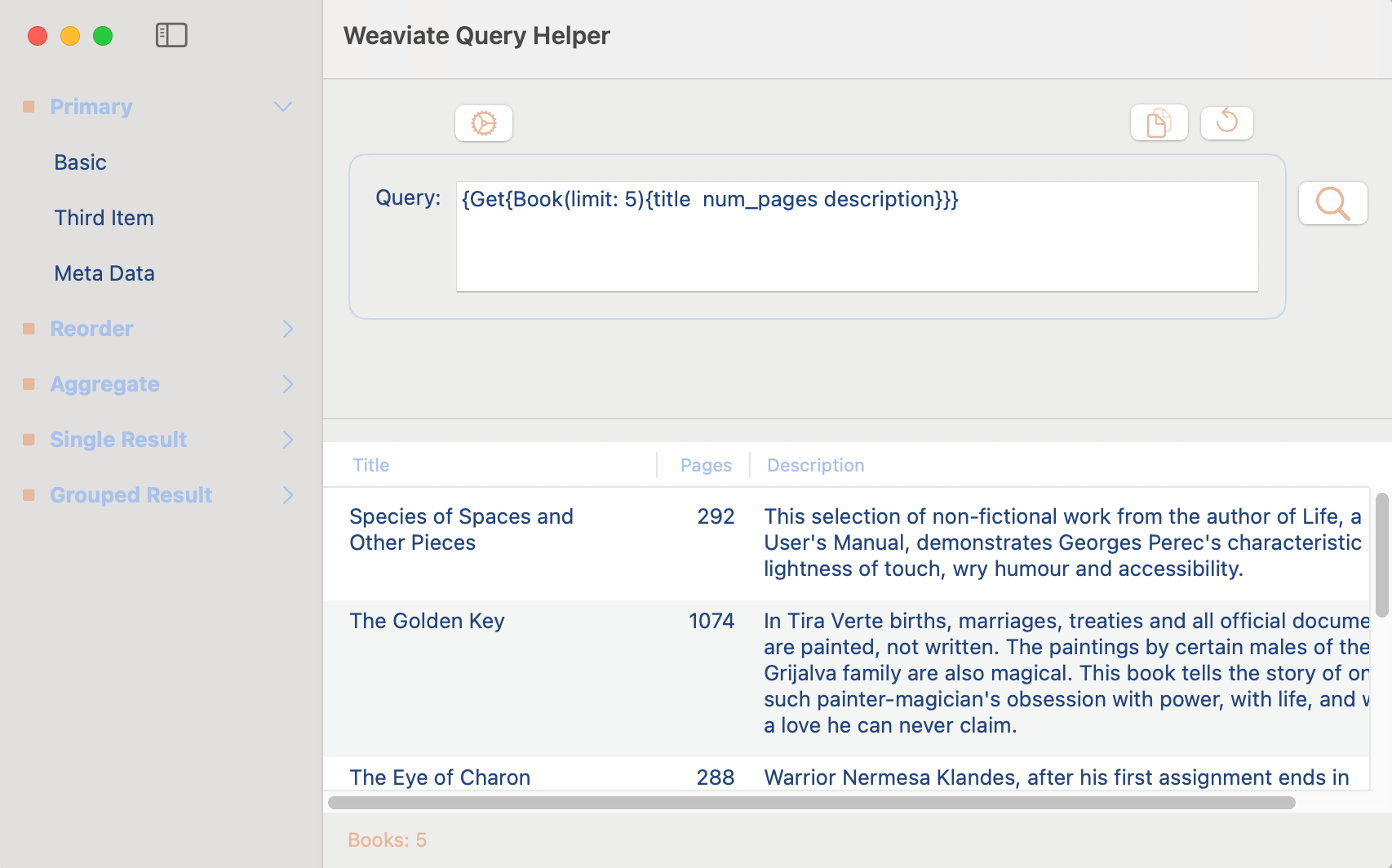
Example: Get the first 5 Books and list the title, number of pages and description.
{
Get {
Book(limit: 5) {
title
num_pages
description
}
}
}
Third Item
Query starting from the third record.
Example: Using the Basic Query as a starter, skip the first two books and start from the book that follows. Example: Starting from the 3rd book: list the title, number of pages and description of the next 5.
{
Get {
Book(limit: 5, offset: 2) {
title
num_pages
description
}
}
}
Meta Data
Show information that extends beyond the initial domain data loaded. This is data generated by the system.
Example: Include ID, creation date, last update date.
{
Get {
Book(limit: 5) {
title
_additional {
id
vector
certainty
score
distance
creationTimeUnix
lastUpdateTimeUnix
}
}
}
}
Reorder
Move Away
Allow users to prioritize similar concepts and deemphasize others. Example: Emphasize “war” themes and deemphasize “romance”.
{
Get {
Book(
limit: 5
nearText: {
concepts: ["Mysteries set in Western Europe"]
distance: 0.6
moveAwayFrom: { concepts: ["romance"], force: 0.45 }
moveTo: { concepts: ["war"], force: 0.85 }
}
) {
title
description
num_pages
}
}
}
Rerank
Change the order in which data elements are displayed based on specific criteria. This is data generated by the system.
Example: The result is reranked to prioritize descriptions that discuss robots.
{
Get {
Book(nearText: { concepts: "science fiction" }, limit: 10) {
title
description
num_pages
categories
_additional {
distance
rerank(property: "description", query: "robot") {
score
}
}
}
}
}
Aggregate
By Category
Group counts based on specific attributes.
Example: Show the number of books for each category.
{
Aggregate {
Book(groupBy: ["categories"]) {
meta {
count
}
groupedBy {
value
}
}
}
}
Grand Total
Total count of the entire dataset.
Example: Show the count of all books in the database.
{
Aggregate {
Book {
meta {
count
}
}
}
}
Single Result
Summary
Summary of a specific query.
Example: Summarize in 10 words books with a mystery theme that occur in Western Europe.
{
Get {
Book(
nearText: { concepts: ["Search for mysteries set in WesternEurope"] }
limit: 5
) {
title
description
_additional {
generate(
singleResult: {
prompt: "Describe the following as a short summary in 10 words:{description}"
}
) {
singleResult
error
}
}
}
}
}
Translate To
Translate data elements or results into different languages.
Example: Search for Mexican books and translate the title into Spanish.
{
Get {
Book(nearText: { concepts: ["What books are Mexican"] }, limit: 5) {
title
description
_additional {
generate(
singleResult: { prompt: "Translate the following in Spanish:{title}" }
) {
singleResult
error
}
}
}
}
}
Translate From/To
Translate data elements or results from different languages to different languages. Example: Ask a question in Spanish and translate the title into Spanish.
{
Get {
Book(nearText: { concepts: ["Que libros son mexicanos"] }, limit: 5) {
title
description
_additional {
generate(
singleResult: { prompt: "Translate the following in Spanish:{title}" }
) {
singleResult
error
}
}
}
}
}
Grouped Result
Grouped Result
Perform prompt on all records retrieved from another prompt. Example: Search for books about the governments in Europe.
Summarize what the leaders of the result have in common.
{
Get {
Book(nearText: { concepts: ["Governments of Europe"] }, limit: 5) {
title
description
_additional {
generate(
groupedResult: {
task: "What do these leaders have in common, if anything?"
}
) {
groupedResult
error
}
}
}
}
}
Conclusion
Hopefully, you have found this article to be a practical guide to building queries with Weaviate Cloud (WCD) on iOS and macOS, even if you're new to the platform. It simplifies the core concept of vector similarity search, showing you how to find similar data. The article positions Weaviate Cloud as a fully managed service that handles the technical complexities of AI infrastructure, allowing you to focus on developing engaging features like recommendation engines and semantic search.
To help you get started, the guide offers a custom Query Helper Application for Mac users, which provides a hands-on way to test different queries. The article breaks down these queries into distinct categories, from basic data retrieval to more advanced functions like reordering results, summarizing data, and even translating text. This resource provides you with the foundational knowledge and practical tools—including a live testing app and code examples—to start creating your own sophisticated, AI-driven applications with confidence!
Ready to start building?
Check out the Quickstart tutorial, or build amazing apps with a free trial of Weaviate Cloud (WCD).
Don't want to miss another blog post?
Sign up for our bi-weekly newsletter to stay updated!
By submitting, I agree to the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
