
Intro
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has enabled computers to understand the human language. It has shifted the way humans build and interact with computers. Large Language Models (LLMs) underpin the latest developments in NLP and have gained traction in various applications. Cohere is an AI platform that provides its users with access to its LLMs. Cohere gives developers and businesses the ability to implement NLP as part of their toolkit.
Cohere trains their own LLMs for text generation and understanding and serves them via API. You can think of it as a managed LLM service in the cloud, with the ability to customize/finetune them on your dataset.
Cohere + Weaviate
Now, you can combine Cohere’s LLMs with a vector database like Weaviate to get the best of both worlds. More specifically, you can run complex NLP queries at a large scale of millions (and even billions) of text objects and get results back in a blink of an eye.
If you don’t consider a "blink of an eye" as a scientific metric (note: it isn’t!), you can check Weaviate’s benchmarks on some standard datasets.
But until now, getting outputs from Cohere into Weaviate required a few extra steps. This included sending requests to Cohere to vectorize text objects, retrieving the output vectors, and then importing it into Weaviate along with the matching objects.
Text2vec-cohere
Over the last few weeks, we’ve partnered with Cohere to create a new Weaviate module – text2vec-cohere – it allows you to use Cohere’s LLMs to run complex NLP queries straight from Weaviate.
You can learn all about text2vec-cohere from the docs.
And there is a lot that you can do with Cohere, including some very new, exciting developments. drumroll 🥁
Text-understanding multilingual model
Today, Cohere announced the release of the text-understanding multilingual model that supports 100+ languages.
The multilingual model is perfect for search, content aggregation and recommendation, and zero-shot cross-lingual text classification.
There are so many great use cases: Search through a multilingual forum for answers in one language, then use browser translation to output the content in the same language. Search through your resources, documentation, etc., in the readers’ native language. Enable product search in the language(s) that your users are comfortable with.
Multilingual model quick test
After learning from our friends at Cohere that the model can handle over a hundred human languages, I was eager to test it out and see what I could achieve by running a few queries in different languages.
So, I’ve created a small dataset with a few objects with descriptions of animals (squirrels, horses, meerkats, etc.), musical instruments, and vehicles. The descriptions for half of the objects are in English, but the remaining objects are written in other languages like German, Italian, Swedish, Spanish etc.
Then, I took 15 minutes to create a small Python project. It includes two Jupyter Notebooks to import data and query articles.
To follow along, you should:
- set up a new Weaviate instance in WCD
- request a Cohere API key
Then, the notebooks show you how to:
- configure data schema to use the Cohere
embed-multilingual-v2.0model - and import a small (handcrafted) dataset.
Query for musical instruments
Once my setup was ready, I was able to run queries like "What musical instruments do we have?" in Polish
python query.py "jakie mamy instrumenty muzyczne?"
Or a shorter query in Hungarian – "musical instruments?"
python query.py "zenei hangszerek?"
Both queries returned the following objects. Note the guitar content is in Italian, while the Drum content is in English.
[{
"enName":"Guitar",
"name":"Chitarra",
"content": "La chitarra è uno strumento musicale cordofono a pizzico, che può essere suonato con i polpastrelli, con le unghie o con un plettro.",
"_additional":{
"certainty":0.7987224459648132,
"distance":0.4025551
}
},
{
"enName":"Drum",
"name":"Drum",
"content": "The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system, it is a membranophone...",
"_additional":{
"certainty":0.7355101704597473,
"distance":0.52897966
}
}]
Query for small animals
Next, I tried to query for "small animals" in Japanese.
python query.py "小動物"
Which returned three objects about meerkats (each in a different language) and one about squirrels.
[{
"enName": "Meerkat",
"name": "Erdmännchen",
"content": "Das Erdmännchen (Suricata suricatta), auch Surikate oder veraltet Scharrtier genannt, ist eine Säugetierart aus der Familie der Mangusten (Herpestidae).",
"_additional": { "certainty": 0.7455021142959595, "distance": 0.5089958 }
},{
"enName": "Meerkat",
"name": "Surikat",
"content": "Surikat (Suricata suricatta) är ett litet däggdjur som lever i sydvästra Afrika, i Kalahariöknen i Botswana, i Namiböknen i Namibia och Angola samt i Sydafrika.",
"_additional": {"certainty": 0.7168638408184052, "distance": 0.5662723}
},{
"enName": "Meerkat",
"name": "Suricata",
"content": "La suricata (Suricata suricatta) es una especie de mamífero carnívoro de la familia Herpestidae que habita la región del desierto de Kalahari y el Namib en África. La suricata es una de las mangostas más pequeñas.",
"_additional": { "certainty": 0.7151028215885162, "distance": 0.56979436 }
},{
"enName": "Squirrel",
"name": "Hörnchen",
"content": "Die Hörnchen (Sciuridae) sind eine Familie aus der Ordnung der Nagetiere (Rodentia). Unter anderem gehören das Eurasische Eichhörnchen, das Streifenhörnchen und das europäische Ziesel zu dieser Familie.",
"_additional": { "certainty": 0.7129454612731934, "distance": 0.5741091 }
}]
Test conclusion
Even though this was just a small test, the results I received back are great. I never thought it would be this easy to search across documents that are written in different languages.
Over the Christmas break, I will take some time to build a larger app to more thoroughly test the Weaviate + Cohere combo. Something that will come with more data and test for more complex queries and scenarios. 😉
If you have interesting data project ideas, give me a shout on Weaviate community Slack or via Twitter @sebawita.
Project in GitHub
You can find the test project on GitHub. Follow the readme instructions on how to set it up for yourself.
Probably the most interesting part is the query code, which is made of 3 parts:
nearText– parameters where we pass in the query from the userproperties– a list of properties we want back from the databaseclient.query– it takes the above two, and runs a semantic search. Note, how it doesn’t even mention the Cohere model, as all of that is done through configuration.
def semantic_serch(query):
client = _setup.connect_to_weaviate()
nearText = {
"concepts": [query],
"distance": 0.7,
}
properties = [
"name", "content", "enName", "link", "lang",
"_additional {certainty distance}"
]
result = (
client.query
.get("Document", properties)
.with_near_text(nearText)
.with_limit(5)
.do()
)
return result['data']['Get']['Document']
How does this work
It is also important to understand how Weaviate and Cohere communicate with each other.
Weaviate fully automates communication with Cohere’s AI Platform. There are two key scenarios when Weaviate will communicate with Cohere:
- Data import and modifications – to vectorize data objects
- Query time – to vectorize the query
Data import + modifications
When you import (or update) data into Weaviate, Weaviate will:
- Receive the data object
- Send the relevant properties for vectorization to Cohere
- Store the data object and index the vector in Weaviate
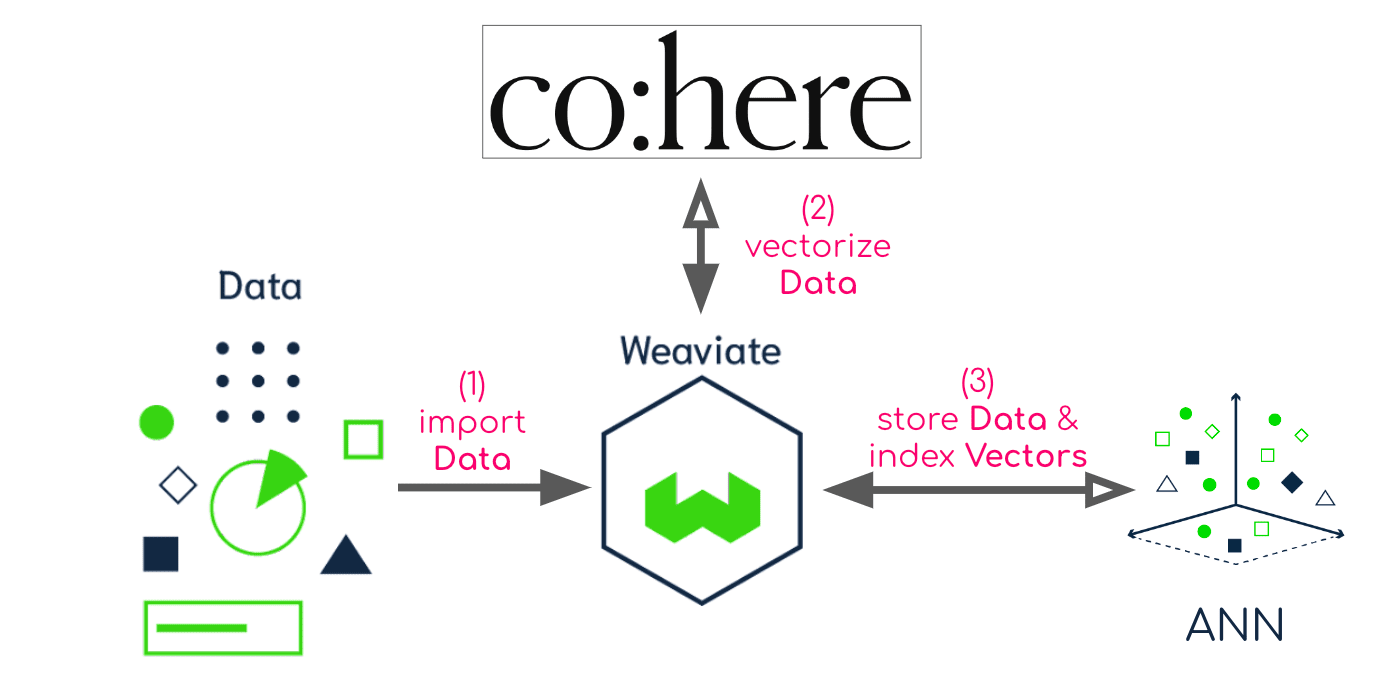
This allows Weaviate to efficiently store and query your data.
Query
When you query Weaviate, Weaviate will:
- Receive the query
- Send the query to Cohere to vectorize it
- Use the returned query vector and search in the vector index
- Return matched objects
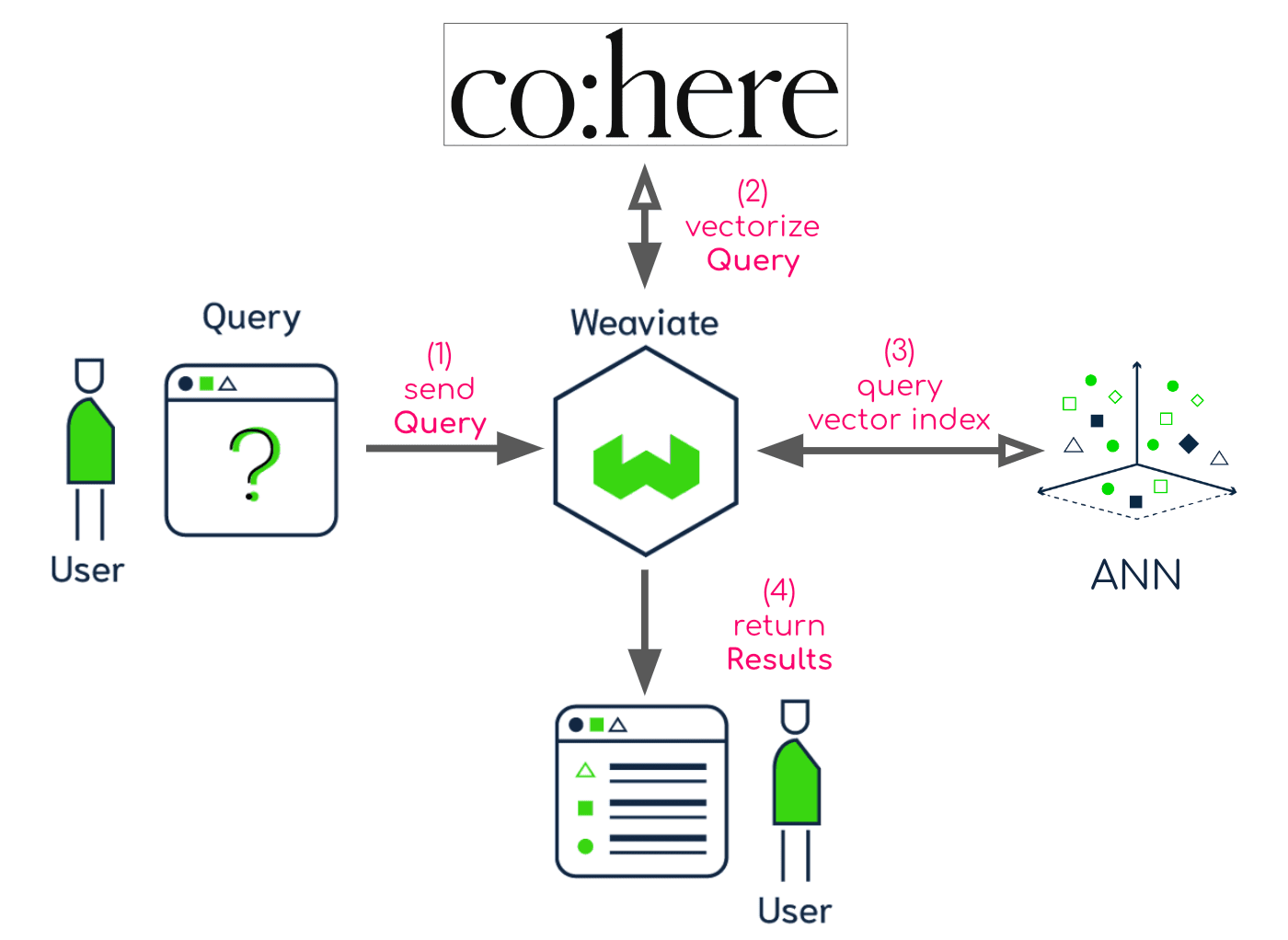
This shows a clear separation of roles:
Cohere– takes care of vectorizing the data, with the power of Large Language ModelsWeaviate– orchestrates the process, stores the data and vectors, and provides production-ready performance.
Full CRUD support
It is worth knowing that Weaviate allows you to continuously modify the data whilst the database remains operational at all times. Exactly what you would expect from any database.
Every time you add new or modify existing objects, Weaviate will obtain new vectors from Cohere and store them with their objects. And if you delete any objects, then Weaviate removes their corresponding vectors from the index.
The best thing is, from the query or data modifications point of view, you don’t need to do anything about the Weaviate ⇔ Cohere coordination.
What next
Check out the text2vec-cohere to learn more about the new module.
Ready to start building?
Check out the Quickstart tutorial, or build amazing apps with a free trial of Weaviate Cloud (WCD).
Don't want to miss another blog post?
Sign up for our bi-weekly newsletter to stay updated!
By submitting, I agree to the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
