❓When using LLMs is unsupervised fine-tuning better than RAG for knowledge-intensive tasks? Should you do both?
If you want to augment an LLM with knowledge of your enterprise data you can do so by augmenting the parametric (finetune) or non-parametric(w/ a vector db like @weaviate_io ) memory.
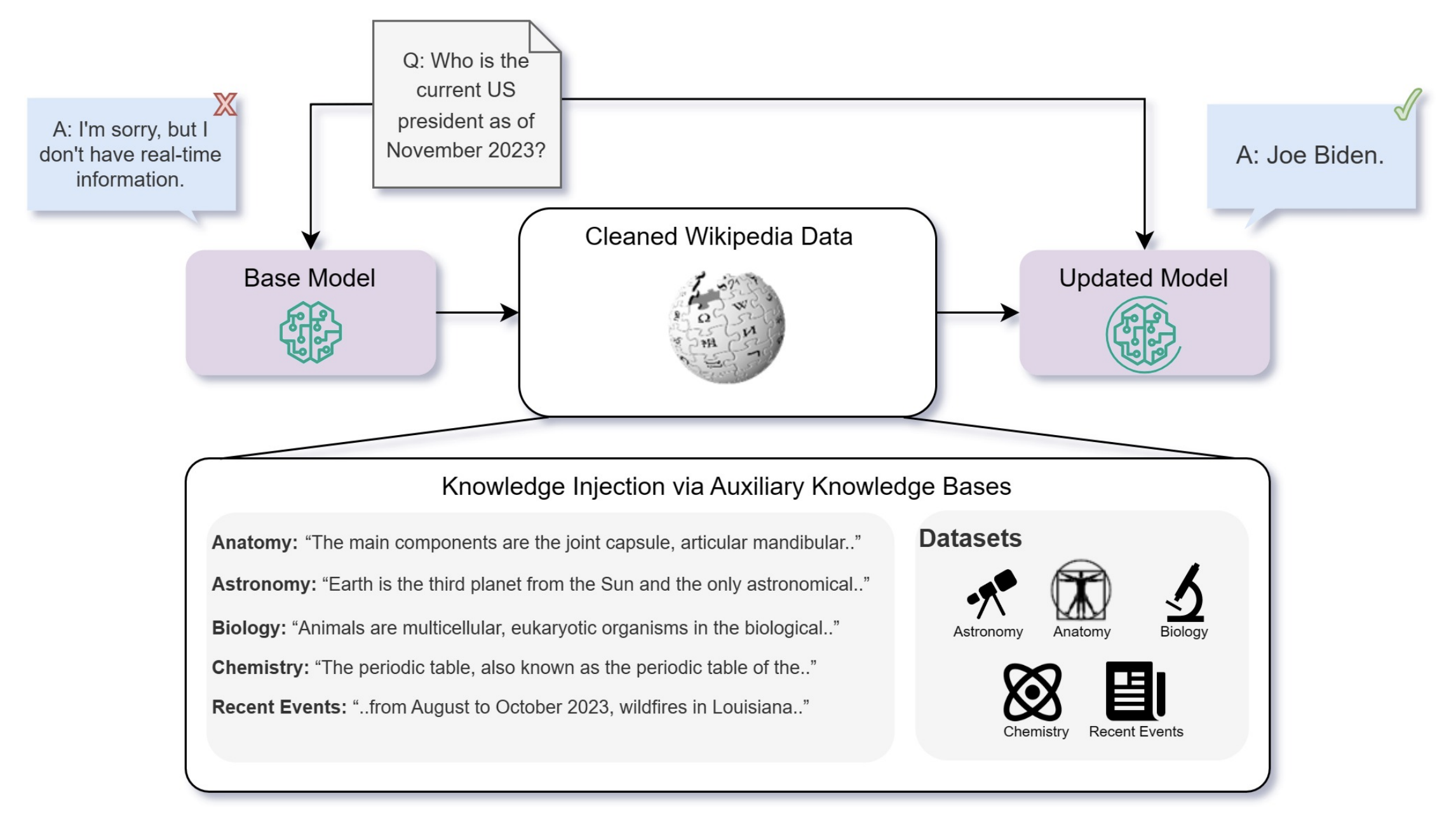
📜Researchers from Microsoft(https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.05934) asked if unsupervised next token prediction finetuning is better than RAG to improve LLM perf. on both seen and unseen QnA tasks?
⏩In Short: RAG is a better way to inject knowledge into LLMs than unsupervised fine-tuning(USFT) and more surprisingly they found that RAG alone is even better than RAG + finetuning. Probably because USFT is not efficiently persisting new knowledge into params.
Would be cool to see a study comparing RAG vs. SFT/Instruction tuning or RLHF.
This improvement in QnA tasks with RAG occurred for both questions in the MMLU dataset as well as on a new dataset of "current events" that the model was not trained on.
📑The details:
Used Mistral, Llama2, Orca2 7B for all assessments.
Only unsupervised finetuning was done - a direct continuation of the pre-training phase - by predicting the next token on the dataset
Used bge-large-en as the embedding model for the RAG component
Finetuning with multiple paraphrases of the same fact provides a significant improvement over the baseline. - To teach pre-trained LLMs new knowledge, the knowledge must be repeated in numerous ways
❌ Limitations/Short-comings:
Only a continuation of the pre-training was assessed - no instruction tuning or RLHF - SFT and RLHF will boost performance further.
Accuracy performance variance is quite high across the experiments - so it's quite hard to determine the statistical significance of results.
Why is the performance of baseline models on future data not 25% for MCQs with 4 choices? - Not truly "unseen" knowledge.
Only straightforward knowledge/fact tasks were assessed - reasoning capabilities were not assessed..
Ready to start building?
Check out the Quickstart tutorial, or build amazing apps with a free trial of Weaviate Cloud (WCD).
Don't want to miss another blog post?
Sign up for our bi-weekly newsletter to stay updated!
By submitting, I agree to the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
