
Weaviate 1.16 introduced the Ref2Vec module. In this article, we give you an overview of what Ref2Vec is and some examples in which it can add value such as recommendations or representing long objects.
What is Ref2Vec?
The name Ref2Vec is short for reference-to-vector, and it offers the ability to vectorize a data object with its cross-references to other objects. The Ref2Vec module currently holds the name ref2vec-centroid because it uses the average, or centroid vector, of the cross-referenced vectors to represent the referencing object. The benefit of this approach is that the referencing object can be characterized from its actions and relationships as well as refined over time.
In one example, we could use Ref2Vec in a Weaviate database containing User and Product classes of objects to produce recommendations. Here, the Product class may include various types of vectorized items, such as shoes, or clothing, and a User could be vectorized by its relationships to Product instances. So a User who has liked 3 shoe Product instances will be represented as the average vector of the 3 shoe Product vectors, whereas another User might be represented by an average vector of whatever Product instances that they liked. This can be used for recommendation, for instance, by treating the averaged vector of the User as a search query in Product objects.
The following image depicts how Ref2Vec aggregates the representations of 3 Product items to represent a User who has purchased a pair of boots, shorts, and Weaviate t-shirt!
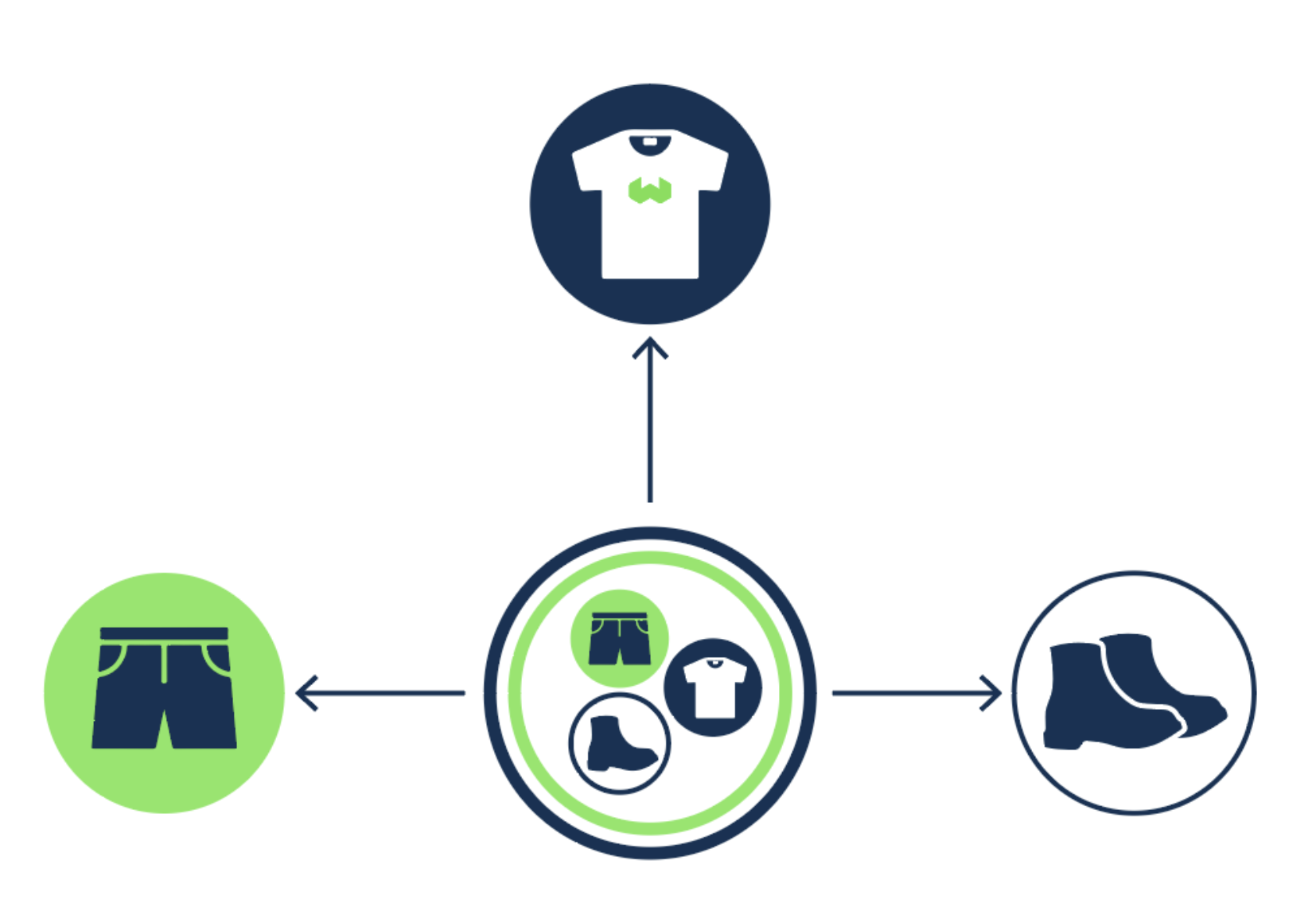
Such a representation of the User, by an aggregation of their cross-references, allows Weaviate to conveniently and immediately learn from each User's preferences and actions to provide improved and up-to-date characterizations. Ref2Vec can in other words capture each User's interests and tendencies across multiple axes, such as product categories or even fashion styles! And by doing so, the resulting recommendations can more closely match the User's product and style preferences.
We envision Ref2Vec to have great potential in multiple application areas. Let's take a look at a few of them in more detail, starting with recommendation systems.
Recommendation in Weaviate
Many of you might primarily know Weaviate as a vector database and search engine, but Weaviate can also power high-quality, lightning-fast recommendations. This is because Recommendation is a very similar task to Search from the perspective of a vector database. Both tasks leverage the ANN index of vector representations to search for a suitable object. The key difference is that in Search, relevance is typically contained entirely within the query. In Recommendation, relevance is additionally dependent on the user, making the query a subjective, user-dependent task rather than an objective task. So if a User searches for "adidas shoes for the summer", not only does Weaviate need to find these particular kinds of shoes, but it also needs to rank them based on relevance to the particular user's interests!
With Ref2Vec, this task is made easier by representing a user's interests by drawing a graph of cross-references from the user to objects the user has engaged with. This gives Weaviate unique points of reference for each user that can be used to rank the search results.
In Weaviate, Classes represent data objects such as Users, Products, or Brands. The vector for an instance of a Class, such as a Product, is obtained from a Machine Learning model's inference of (typically) an image or text description of the Product. Additionally, Weaviate's cross-references enable relations between Classes, such as Users that "liked" a Product. For example, User, Product, and Brand objects may each have a vector representation, symbolic properties like name or price, and relations as shown below.
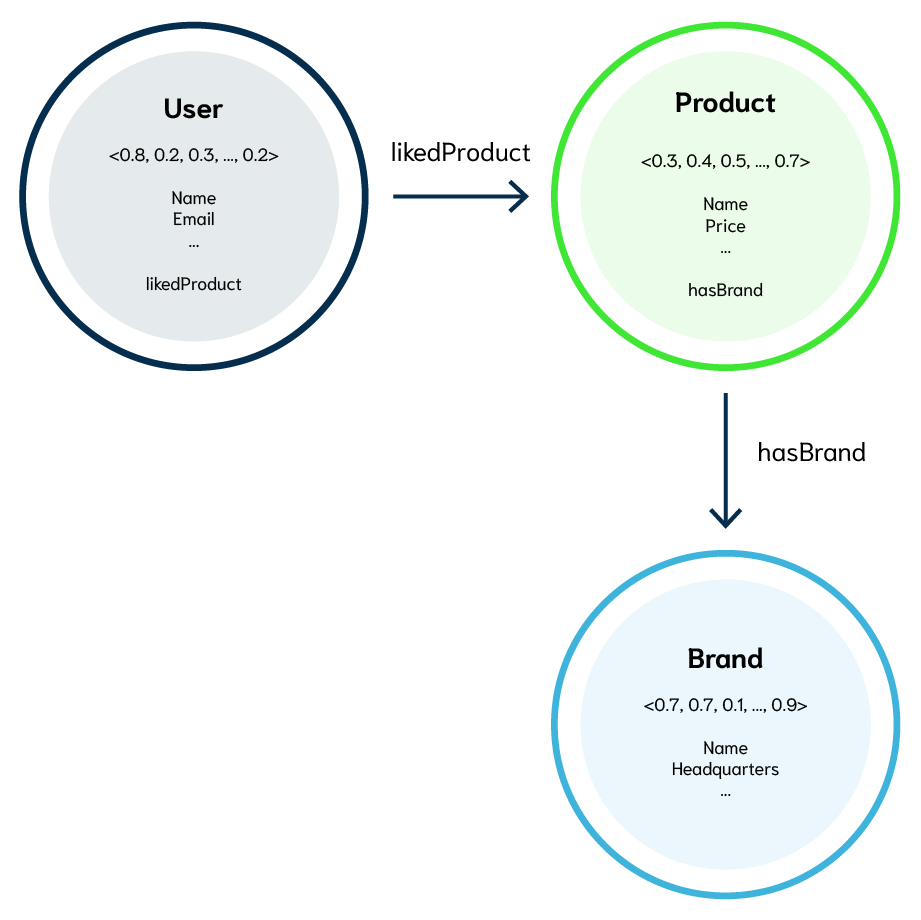
Ref2Vec gives Weaviate another way to vectorize a class, such as the User class, based on their relationships to other classes. This allows Weaviate to quickly create up-to-date representations of users based on their relationships such as recent interactions. If a user clicks on 3 shoe images on an e-commerce store, it is a safe bet that they want to see more shoes. Ref2Vec captures this intuition by calculating vectors that aggregate each User's interaction with another class.
The below animation visualizes a real example of this in e-Commerce images. The demo is organized such that user interactions are outlined with a green box and moved to the top-left of the grid. The nearest neighbors to the ref2vec-centroid are then arranged from left-to-right top-down.
This animation shows how selecting multiple backpacks (such as two school-style book bags) can help personalize the user's recommendations (so showing more backpacks in a similar style rather than the duffle bags). We also see here how selecting multiple digital LED screen watches moves results away from analog watches. In other words, the User vector is being updated in real-time here to take into account their preferences and actions, which helps to produce more relevant results at speed. Another benefit of Ref2Vec is that this calculation is not compute-heavy, leading to low overhead.
With Ref2Vec, you can use Weaviate to provide Recommendation with "user-as-query". This is a very common and powerful way to build Home Feed style features in apps. This can be done by sending queries like this to Weaviate:
{
Get {
Product (
nearObject: {
id: "8abc5-4d5..." # id for the User object with vector defined by ref2vec-centroid
}
) {
product_name
price
}
}
}
This short query encapsulates the power of Ref2Vec. Although all the query does is provide the ID of the User object, Ref2Vec has done the hard work by inferring a centroid vector from the User's references to other vectors. And as the set of references continues to evolve, the Ref2Vec vectors will continue to evolve also, ensuring that the User vector remains up-to-date with their latest interests.
Whether your goal is to construct a Home Feed interface for users or to pair with search queries, Ref2Vec provides a strong foundation to enable Recommendation with fairly low overhead. For example, it can achieve personalized re-ranking, also known as a session-based recommendation, without persisting user data over a long sequence of interactions. A new user could have personalization available after a few interactions on the app which will help them quickly settle in and feel at home, helping to overcome what is known as the cold-start problem.
Representing long objects
One of the most outstanding problems in Search technology is finding suitable representations for long objects. In this sense, "long" is used to describe text documents that significantly exceed the 512 token input limit on Deep Transformer Neural Networks. This problem is a large part of what motivates our interest in Hybrid Search techniques that combine the flexibility of Vector Search with the sparse BM25 word counting algorithm well suited for >512 token text sequences. We think Ref2Vec can also help address this challenge.
To be clear, Weaviate already offers a solution to represent long documents with Cross-References! As an example, the Wikipedia Demo breaks the long Wikipedia articles into a (Paragraph, inArticle, Article) data schema in which each Paragraph contains less than 512 tokens of text. This allows us to combine the title of the Article with the vector search in the Paragraph vectors in Weaviate with the following query:
{
Get {
Paragraph(
nearText: {
concepts: ["What was Obama's legacy?"],
}
where: {
operator: Equal,
path: ["inArticle", "Article", "title"]
valueText: "Barack Obama"
}
) {
content
order
title
}
}
}
So Weaviate already has a strong solution to long documents in play. However, what if we are searching through Scientific Papers, Legal contracts, or Screenplays such that we need to make long-range references between the Paragraphs?
In this case, Ref2Vec can be used to average the vectors that represent each Paragraph to form the representation of the referencing Article Class. In other words, each Article instance would refer to constituent Paragraph instances, and the Ref2Vec module would calculate the vector of the Article as the centroid of the Paragraph vectors. We can then search directly through these Articles with an aggregated vector representation from each Wikipedia Article, thus helping to identify full articles that best match the query.
More Coming Soon
We are very excited about the potential of Ref2Vec, and how it leverages existing symbolic data to augment vector searches in a new way. One of my favorite articles about Weaviate is Bob van Luijt's "The AI-First Database Ecosystem". In this article, Bob describes emerging waves of database technology; from SQL, to NoSQL, and now, AI-first databases that focus "on data that is processed by a machine learning model first, where the AI models help in processing, storing and searching through the data as opposed to traditional ways".
Although Weaviate puts Machine Learning data representations first, this doesn't mean we discard symbolic data and many features of previous systems. Rather, we are actively searching for how symbolic data can improve neural functionality and vice versa.
Weaviate is a database that supports data structures like inverted index structures of categorical properties. Weaviate can integrate symbolic properties such as "colour" in the HNSW vector search algorithm to enable more efficient and guided search. This is called pre-filtering to describe applying the symbolic filter prior / during the search rather than simply after the nearest neighbors have been returned in post-filtering. Weaviate has clear applications of symbolic properties in vector search, but we have another symbolic data type that we hadn't yet leveraged in vector search – Relational Structure.
Ref2Vec-Centroid goes some way to harness the joint power of vector search combined with relational structure, by making it easier to derive object vectors from relationships. As you have seen above, we think Ref2Vec can add value for use cases such as recommendations, re-ranking, overcoming the cold start problem and representing long objects. We are also excited to see what you build with Ref2Vec, and excited to build on this module with its future iterations.
Speaking of which, we have another blog post coming soon on the development directions of Ref2Vec for the future. We will discuss topics such as collaborative filtering, multiple centroids, graph neural networks, and more on re-ranking with Ref2Vec. Stay tuned!
Ready to start building?
Check out the Quickstart tutorial, or build amazing apps with a free trial of Weaviate Cloud (WCD).
Don't want to miss another blog post?
Sign up for our bi-weekly newsletter to stay updated!
By submitting, I agree to the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
