Flat index in depth
The "flat" index is a simple and efficient vector index type that is best suited for small collections of vectors.
Key ideas
The flat index is a very simple vector index that mimics a "map" data type. It simply stores the location of each vector, such that a search can be done by comparing the query vector to each vector in the collection. As you might expect, this leads to very low resource requirements, at the cost of search speed as the number of vectors increases.
Where this index type shines is in large use cases where there are a high number of small collections, such as one for each end-user in a multi-tenant environment. A basic example may be a notes application, where each end user has their own collection of notes.
In such an environment, each end user will be treated as a "tenant", in a multi-tenant collection, and each tenant will have their own vector index. This is a perfect use case for the flat index.
Trade-offs
The key compromise with the flat index is that it is not scalable. As the number of vectors in the collection increases, the search time will increase linearly, as each vector must be compared to the query vector.
Resource requirements
The flat index has very low memory requirements, as it only needs to store the location to the vector, and not the vector itself.
This can be very beneficial as the overall database grows, especially if the growth is primarily in the number of indexes (tenants), rather than the number of vectors in each index.
Distance metric
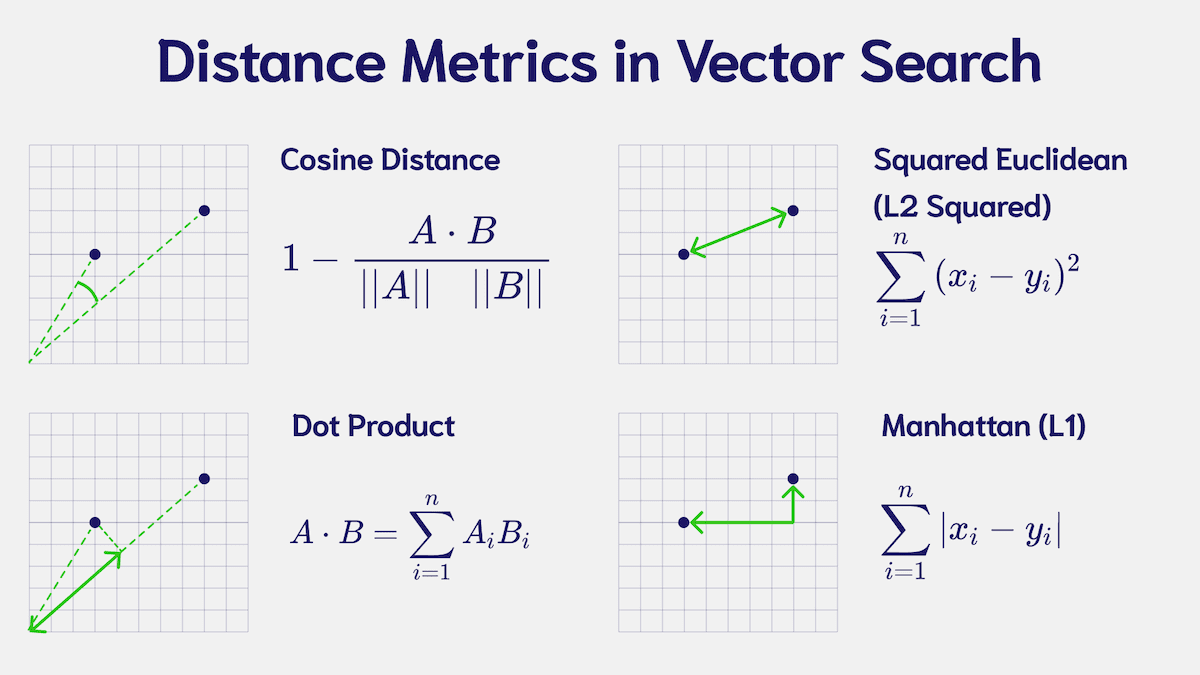
The distance metric used in the index determines how the distance between vectors is calculated.
You must choose a metric that suits the vectors in your collection. To find this, consult the documentation of the model that generated your vectors.
Weaviate's default metric is cosine, but you can also use any number of other available metrics.
If you are unsure, the cosine distance is a good, robust, default choice that is used by a majority of models.
Quantization
Enabling quantization with the flat reduces the search time by using compressed vectors. Note that the full vector is still stored, which is used to rescore the vectors after they are fetched during initial search.
This can improve the search speed to mitigate the linear increase in search time as the number of vectors increases. However, the scalability of the flat index is still limited.
Learn more about quantization with this Weaviate Academy course.
Configure flat index in Weaviate
Each of these parameters can be provided when creating a collection in Weaviate. Note that the vector_cache_max_objects is only used if quantization is enabled with vector caching enabled within it.
Code example
from weaviate.classes.config import Configure, VectorDistances
client.collections.create(
name=collection_name,
# ... other parameters
vector_index_config=Configure.VectorIndex.flat(
distance_metric=VectorDistances.COSINE, # Distance metric
quantizer=Configure.VectorIndex.Quantizer.bq(cache=True), # Quantizer configuration
vector_cache_max_objects=1000000, # Maximum number of objects in the cache
)
)
Further resources
- Concepts: Vector index
- References: Vector index parameters
- How-to manage collections
- Weaviate Academy: Compression
Questions and feedback
If you have any questions or feedback, let us know in the user forum.
