Dynamic index in depth
The "dynamic" index is a "best of both worlds" approach that combines the benefits of the hnsw and flat indexes.
ASYNC_INDEXINGDynamic indexes require asynchronous indexing. To enable asynchronous indexing in a self-hosted Weaviate instance, set the ASYNC_INDEXING environment variable to true. If your instance is hosted in Weaviate Cloud, use the Weaviate Cloud console to enable asynchronous indexing.
Key ideas
Simply put, the dynamic index is a flat index that is automatically converted to an hnsw index when the number of vectors in the collection exceeds a predetermined threshold (10,000 by default).
The motivation for this is that the flat index is very efficient for small collections, but its search time increases linearly with the number of vectors in the collection. The hnsw index, on the other hand, is more efficient for large collections, but includes a memory overhead with little benefit for small collections.
The dynamic index is a good choice if you do not know how big the size of each collection will be, or if you expect some tenants to grow much larger than others.
In a multi-tenancy configuration, this will mean that all tenants will start with the flat index, but will automatically switch to the hnsw index when the number of vectors in the collection exceeds the threshold.
Currently, this is a one-way conversion, meaning that once the index is converted to hnsw, it will not be converted back to flat if it subsequently falls below the threshold.
Distance metric
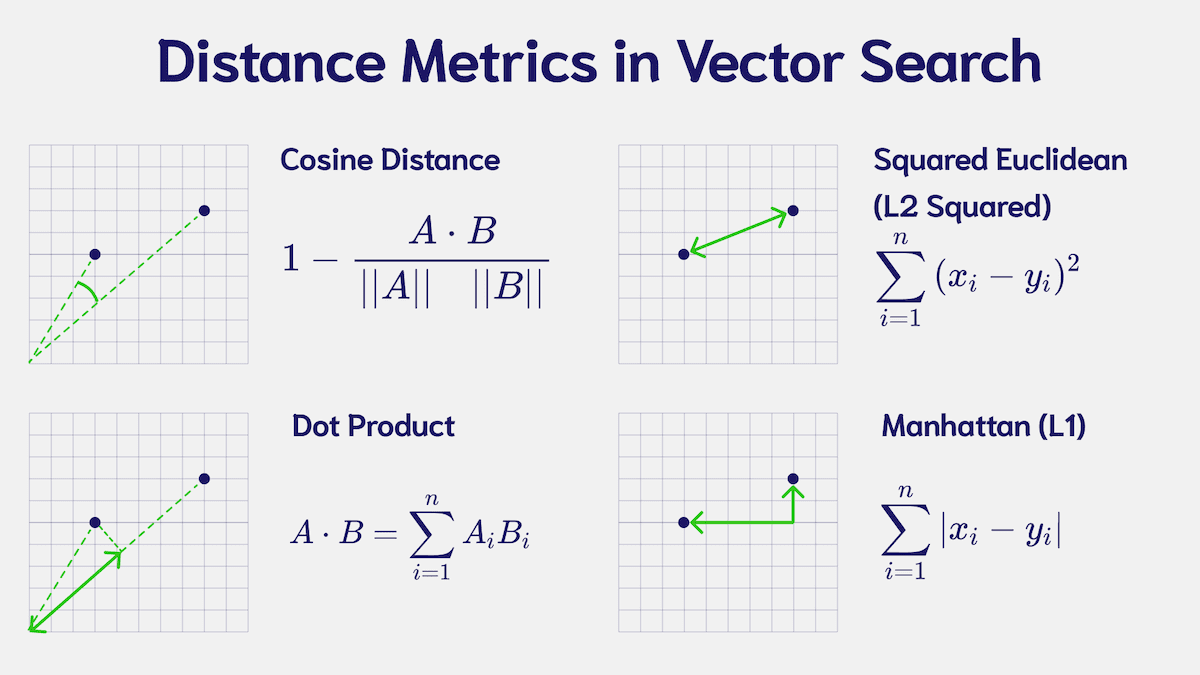
The distance metric used in the index determines how the distance between vectors is calculated. In an HNSW index, it impacts where each vector is placed in the graph.
You must choose a metric that suits the vectors in your collection. To find this, consult the documentation of the model that generated your vectors.
Weaviate's default metric is cosine, but you can also use any number of other available metrics.
If you are unsure, the cosine distance is a good, robust, default choice that is used by a majority of models.
Configure dynamic index in Weaviate
Each of these parameters can be provided when creating a collection in Weaviate. Note that the vector_cache_max_objects is only used if quantization is enabled with vector caching enabled within it.
Basic configuration
Set a collection to use the dynamic index as shown below.
from weaviate.classes.config import Configure
client.collections.create(
name=collection_name,
# ... other parameters
multi_tenancy_config=Configure.multi_tenancy(enabled=True), # Dyanmic index works well with multi-tenancy set-ups
vector_index_config=Configure.VectorIndex.dynamic()
)
Custom configuration
You can set the threshold at which the flat index will be converted to hnsw.
Additionally, you can specify any of the flat and hnsw index parameters that will be used depending on the state of the index.
from weaviate.classes.config import Configure, VectorDistances
client.collections.create(
name=collection_name,
# ... other parameters
multi_tenancy_config=Configure.multi_tenancy( # Dyanmic index works well with multi-tenancy set-ups
enabled=True,
auto_tenant_creation=True,
auto_tenant_activation=True,
),
vector_index_config=Configure.VectorIndex.dynamic(
distance_metric=VectorDistances.COSINE, # Distance metric
threshold=25000, # Threshold for switching to dynamic index
hnsw=Configure.VectorIndex.hnsw(
# Your preferred HNSW configuration
),
flat=Configure.VectorIndex.flat(
# Your preferred flat configuration
),
)
)
Further resources
- Concepts: Vector index
- References: Vector index parameters
- How-to manage collections
- Weaviate Academy: Compression
Questions and feedback
If you have any questions or feedback, let us know in the user forum.
