Additional properties (metadata)
Various 'additional properties', also called 'metadata', can be retrieved in queries.
Available additional properties
The fields id, vector, certainty, distance, featureProjection and classification are available by default.
Further additional properties may be available for each query, depending on the query type as well as enabled Weaviate modules.
Note that only the id is available from cross-referenced objects.
Requesting additional properties
In GraphQL queries, all additional properties to be retrieved can be set through the reserved _additional{} property.
Each of the client libraries may handle this differently. See the examples below.
Usage example
An example query getting the UUID and the distance.
- Python Client v4
- Python Client v3
- JS/TS Client v2
- Go
- Java
- Curl
- GraphQL
import weaviate
import weaviate.classes as wvc
import os
client = weaviate.connect_to_local()
try:
articles = client.collections.get("Article")
response = articles.query.near_text(
query="fashion",
limit=5,
return_metadata=wvc.query.MetadataQuery(distance=True)
)
for o in response.objects:
print(o.metadata.distance) # Inspect metadata
print(o.uuid) # Inspect UUID (returned by default)
print(o.properties) # Inspect returned objects
finally:
client.close()
import weaviate
client = weaviate.Client("http://localhost:8080")
near_text_filter = {
"concepts": ["fashion"]
}
query_result = (
client.query
.get("Article", "title")
.with_additional(["id", "distance"])
.with_near_text(near_text_filter)
.do()
)
print(query_result)
import weaviate from 'weaviate-ts-client';
const client = weaviate.client({
scheme: 'http',
host: 'localhost:8080',
});
const response = await client.graphql
.get()
.withClassName('Article')
.withNearText({ concepts: ['fashion'] })
.withFields('title _additional { id distance }')
.do();
console.log(response);
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/weaviate/weaviate-go-client/v5/weaviate"
"github.com/weaviate/weaviate-go-client/v5/weaviate/graphql"
)
func main() {
cfg := weaviate.Config{
Host: "localhost:8080",
Scheme: "http",
}
client, err := weaviate.NewClient(cfg)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
className := "Article"
fields := []graphql.Field{
{Name: "title"},
{Name: "_additional", Fields: []graphql.Field{
{Name: "id"},
{Name: "distance"},
}},
}
explore := client.GraphQL().NearTextArgBuilder().
WithConcepts([]string{"fashion"})
ctx := context.Background()
result, err := client.GraphQL().Get().
WithClassName(className).
WithFields(fields...).
WithNearText(explore).
Do(ctx)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%v", result)
}
package io.weaviate;
import io.weaviate.client.Config;
import io.weaviate.client.WeaviateClient;
import io.weaviate.client.base.Result;
import io.weaviate.client.v1.graphql.model.GraphQLResponse;
import io.weaviate.client.v1.graphql.query.argument.NearTextArgument;
import io.weaviate.client.v1.graphql.query.fields.Field;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Config config = new Config("http", "localhost:8080");
WeaviateClient client = new WeaviateClient(config);
Field title = Field.builder()
.name("title")
.build();
Field _additional = Field.builder()
.name("_additional")
.fields(new Field[]{
Field.builder().name("id").build(),
Field.builder().name("distance").build()
}).build();
NearTextArgument explore = client.graphQL().arguments().nearTextArgBuilder()
.concepts(new String[]{ "fashion" })
.build();
Result<GraphQLResponse> result = client.graphQL().get()
.withClassName("Article")
.withFields(title, _additional)
.withNearText(explore)
.run();
if (result.hasErrors()) {
System.out.println(result.getError());
return;
}
System.out.println(result.getResult());
}
}
echo '{
"query": "{
Get {
Article (
nearText: {
concepts: [\"fashion\"],
}
) {
title
_additional {
id
distance
}
}
}
}"
}' | curl \
-X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer learn-weaviate' \
-H "X-OpenAI-Api-Key: $OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-d @- \
https://edu-demo.weaviate.network/v1/graphql
{
Get {
Article (
nearText: {
concepts: ["fashion"],
}
) {
title
_additional {
id
distance
}
}
}
}
Expected response
{
"data": {
"Get": {
"Article": [
{
"_additional": {
"distance": 0.15422738,
"id": "e76ec9ae-1b84-3995-939a-1365b2215312"
},
"title": "How to Dress Up For an Untraditional Holiday Season"
},
{
"_additional": {
"distance": 0.15683109,
"id": "a2d51619-dd22-337a-8950-e1a407dab3d2"
},
"title": "2020's biggest fashion trends reflect a world in crisis"
},
...
]
}
}
}
Additional properties
id
Use the id field to fetch the object UUID.
vector
Use the vector field to fetch the vector embedding of the data object
generate
The generate field can be used to perform retrieval augmented generation.
A generate query will cause corresponding additional result fields to be available, such as singleResult, groupedResult and error.
For examples, see the related how-to page.
rerank
The rerank field can be used to reorder the search results. It accepts two parameters:
| Parameter | Required | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
property | yes | string | Which property to pass to the reranker. For example, you may want to run a similarity search on a Products collection, then rerank specifically on the Name field. |
query | no | string | Optionally specify a different query. |
A rerank query will cause corresponding additional score field to be available.
For examples, see the related how-to page.
creationTimeUnix
Use the creationTimeUnix field to fetch the data object creation timestamp.
lastUpdateTimeUnix
Use the lastUpdateTimeUnix field to fetch the data object last updated timestamp.
Vector search metadata
Use the distance or certainty field to fetch a vector similarity metric between the query vector and each result of a vector search.
Distance
v1.14.0Distance is the raw distance determined as part of the vector search, displayed in the same unit as the distance metric used.
See the full overview of distance metrics and the expected distance ranges.
A lower value for a distance always means that two vectors are closer to one another than a higher value.
Certainty (only for cosine distance)
Certainty is an opinionated measure that always returns a number between 0 and 1. It is therefore only usable with fixed-range distance metrics, such as cosine.
Keyword search metadata
Use the score and explainScore field to fetch the scores and explanations of each result of a keyword (BM25) search.
Score
The score will be the BM25F score of the result. Note that this score is relative to the dataset and query.
ExplainScore
The explainScore will explain the BM25F score of the result, broken down into its components. This can be used to understand why a result was scored the way it was.
Hybrid search metadata
Use the score and explainScore field to fetch the scores and explanations of each result of a hybrid search.
Score
The score will be the hybrid score of the result, based on the nominated fusion algorithm. Note that this score is relative to the dataset and query.
ExplainScore
The explainScore will be the hybrid score of the result, broken down into its vector and keyword search components. This can be used to understand why a result was scored the way it was.
Classification
When a data-object has been subjected to classification, you can get additional information about how the object was classified by running the following command:
- Python
- JS/TS Client v2
- Go
- Java
- Curl
- GraphQL
import weaviate
client = weaviate.Client("http://localhost:8080")
near_text_filter = {
"concepts": ["fashion"]
}
additional_props = {
"classification" : ["basedOn", "classifiedFields", "completed", "id"]
}
query_result = (
client.query
.get("Article", "title")
.with_additional(additional_props)
.with_near_text(near_text_filter)
.do()
)
print(query_result)
import weaviate from 'weaviate-ts-client';
const client = weaviate.client({
scheme: 'http',
host: 'localhost:8080',
});
const response = await client.graphql
.get()
.withClassName('Article')
.withFields('title _additional { classification { basedOn classifiedFields completed id scope } }')
.do();
console.log(response);
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/weaviate/weaviate-go-client/v5/weaviate"
"github.com/weaviate/weaviate-go-client/v5/weaviate/graphql"
)
func main() {
cfg := weaviate.Config{
Host: "localhost:8080",
Scheme: "http",
}
client, err := weaviate.NewClient(cfg)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
className := "Article"
title := graphql.Field{Name: "title"}
_additional := graphql.Field{Name: "_additional", Fields: []graphql.Field{
{Name: "classification", Fields: []graphql.Field{
{Name: "basedOn"},
{Name: "classifiedFields"},
{Name: "completed"},
{Name: "completed"},
}},
}}
ctx := context.Background()
result, err := client.GraphQL().Get().
WithClassName(className).
WithFields(title, _additional).
Do(ctx)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%v", result)
}
package io.weaviate;
import io.weaviate.client.Config;
import io.weaviate.client.WeaviateClient;
import io.weaviate.client.base.Result;
import io.weaviate.client.v1.graphql.model.GraphQLResponse;
import io.weaviate.client.v1.graphql.query.fields.Field;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Config config = new Config("http", "localhost:8080");
WeaviateClient client = new WeaviateClient(config);
Field title = Field.builder()
.name("title")
.build();
Field _additional = Field.builder()
.name("_additional")
.fields(new Field[]{
Field.builder()
.name("classification")
.fields(new Field[]{
Field.builder().name("basedOn").build(),
Field.builder().name("classifiedFields").build(),
Field.builder().name("completed").build(),
Field.builder().name("id").build(),
Field.builder().name("scope").build()
}).build()
}).build();
Result<GraphQLResponse> result = client.graphQL().get()
.withClassName("Article")
.withFields(title, _additional)
.run();
if (result.hasErrors()) {
System.out.println(result.getError());
return;
}
System.out.println(result.getResult());
}
}
echo '{
"query": "{
Get {
Article (
nearText: {
concepts: [\"fashion\"],
}
) {
title
_additional {
classification {
basedOn
classifiedFields
completed
id
scope
}
}
}
}
}"
}' | curl \
-X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer learn-weaviate' \
-H "X-OpenAI-Api-Key: $OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-d @- \
https://edu-demo.weaviate.network/v1/graphql
{
Get {
Article (
nearText: {
concepts: ["fashion"],
}
) {
title
_additional {
classification {
basedOn
classifiedFields
completed
id
scope
}
}
}
}
}
Feature Projection
Use feature projection to reduce the results' vectors to 2d or 3d for easy visualization. Currently t-SNE is used.
To tweak the feature projection optional parameters (currently GraphQL-only) can be provided. The values and their defaults are:
| Parameter | Type | Default | Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
dimensions | int | 2 | Target dimensionality, usually 2 or 3 |
algorithm | string | tsne | Algorithm to be used, currently supported: tsne |
perplexity | int | min(5, len(results)-1) | The t-SNE perplexity value, must be smaller than the n-1 where n is the number of results to be visualized |
learningRate | int | 25 | The t-SNE learning rate |
iterations | int | 100 | The number of iterations the t-SNE algorithm runs. Higher values lead to more stable results at the cost of a larger response time |
An example with default settings:
- Python
- JS/TS Client v2
- Go
- Java
- Curl
- GraphQL
import weaviate
client = weaviate.Client("http://localhost:8080")
near_text_filter = {
"concepts": ["music"],
"moveTo": {
"concepts": ["beatles"],
"force": 0.5
}
}
additional_clause = {
"featureProjection": [
"vector"
]
}
additional_setting = {
"dimensions": 2
}
query_result = (
client.query
.get("Article", "title")
.with_near_text(near_text_filter)
.with_additional(
(additional_clause, additional_setting)
)
.do()
)
print(query_result)
import weaviate from 'weaviate-ts-client';
const client = weaviate.client({
scheme: 'http',
host: 'localhost:8080',
});
const response = await client.graphql
.get()
.withClassName('Article')
.withFields('title _additional {featureProjection(dimensions: 2) { vector }}')
.withNearText({
concepts:['music'],
moveTo: {
concepts: ['beatles'],
force: 0.5,
},
})
.withLimit(12)
.do();
console.log(response);
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/weaviate/weaviate-go-client/v5/weaviate"
"github.com/weaviate/weaviate-go-client/v5/weaviate/graphql"
)
func main() {
cfg := weaviate.Config{
Host: "localhost:8080",
Scheme: "http",
}
client, err := weaviate.NewClient(cfg)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
className := "Article"
fields := []graphql.Field{
{Name: "title"},
{Name: "_additional", Fields: []graphql.Field{
{Name: "featureProjection(dimensions: 2)", Fields: []graphql.Field{
{Name: "vector"},
}},
}},
}
concepts := []string{"music"}
moveTo := &graphql.MoveParameters{
Concepts: []string{"beatles"},
Force: 0.5,
}
nearText := client.GraphQL().NearTextArgBuilder().
WithConcepts(concepts).
WithMoveTo(moveTo)
ctx := context.Background()
result, err := client.GraphQL().Get().
WithClassName(className).
WithFields(fields...).
WithNearText(nearText).
WithLimit(12).
Do(ctx)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%v", result)
}
package io.weaviate;
import io.weaviate.client.Config;
import io.weaviate.client.WeaviateClient;
import io.weaviate.client.base.Result;
import io.weaviate.client.v1.graphql.model.GraphQLResponse;
import io.weaviate.client.v1.graphql.query.argument.NearTextArgument;
import io.weaviate.client.v1.graphql.query.argument.NearTextMoveParameters;
import io.weaviate.client.v1.graphql.query.fields.Field;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Config config = new Config("http", "localhost:8080");
WeaviateClient client = new WeaviateClient(config);
String className = "Article";
Field title = Field.builder().name("title").build();
Field _additional = Field.builder()
.name("_additional")
.fields(new Field[]{
Field.builder()
.name("featureProjection(dimensions: 2)")
.fields(new Field[]{
Field.builder().name("vector").build()
}).build()
}).build();
String[] concepts = new String[]{ "music" };
NearTextMoveParameters moveTo = client.graphQL().arguments().nearTextMoveParameterBuilder()
.concepts(new String[]{ "beatles" }).force(0.5f).build();
NearTextArgument nearText = client.graphQL().arguments().nearTextArgBuilder()
.concepts(concepts)
.moveTo(moveTo)
.build();
Result<GraphQLResponse> result = client.graphQL().get()
.withClassName(className)
.withFields(title, _additional)
.withNearText(nearText)
.withLimit(12)
.run();
if (result.hasErrors()) {
System.out.println(result.getError());
return;
}
System.out.println(result.getResult());
}
}
echo '{
"query": "{
Get {
Article (
nearText:{
concepts:[\"music\"],
moveTo: {
concepts: [\"beatles\"],
force: 0.5
}
}
) {
title
_additional {
featureProjection(dimensions: 2) {
vector
}
}
}
}
}"
}' | curl \
-X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer learn-weaviate' \
-H "X-OpenAI-Api-Key: $OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-d @- \
https://edu-demo.weaviate.network/v1/graphql
{
Get {
Article (
nearText: {
concepts:["music"],
moveTo: {
concepts: ["beatles"],
force: 0.5
}
}
) {
title
_additional {
featureProjection(dimensions: 2) {
vector
}
}
}
}
}
Expected response
{
"data": {
"Get": {
"Article": [
{
"_additional": {
"featureProjection": {
"vector": [
-115.17981,
-16.873344
]
}
},
"title": "Opinion | John Lennon Told Them \u2018Girls Don\u2019t Play Guitar.\u2019 He Was So Wrong."
},
{
"_additional": {
"featureProjection": {
"vector": [
-117.78348,
-21.845968
]
}
},
"title": "Opinion | John Lennon Told Them \u2018Girls Don\u2019t Play Guitar.\u2019 He Was So Wrong."
},
...
]
}
}
}
The above result can be plotted as follows (where the result in red is the first result):
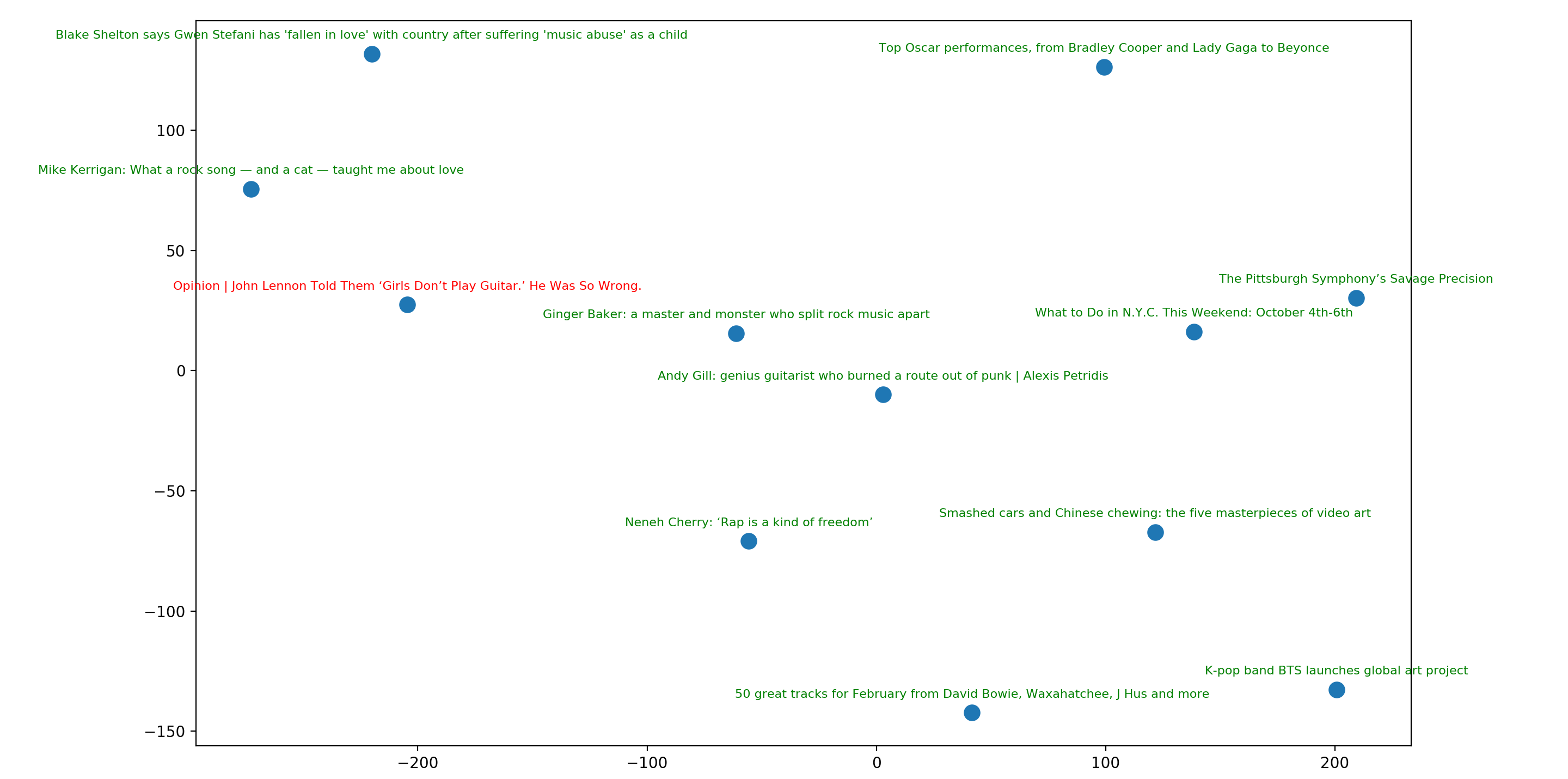
best practices and notes
- Due to the O(n^2) complexity of the
t-SNEalgorithm, we recommend to keep the request size at or below 100 items. t-SNEis non-deterministic and lossy, and happens in real-time per query. The dimensions returned have no meaning across queries.- Due to the relatively high cost of the underlying algorithm, we recommend to limit requests including a
featureProjectionin high-load situations where response time matters. Avoid parallel requests including afeatureProjection, so that some threads stay available to serve other, time-critical requests.
Questions and feedback
If you have any questions or feedback, let us know in the user forum.
