Overview
Why embedding model selection matters
Embedding models are AI models that capture “meanings” of objects. This earlier module on AI models showed that embedding models can do this by turning text, images, audio and more into a sequence of numbers.
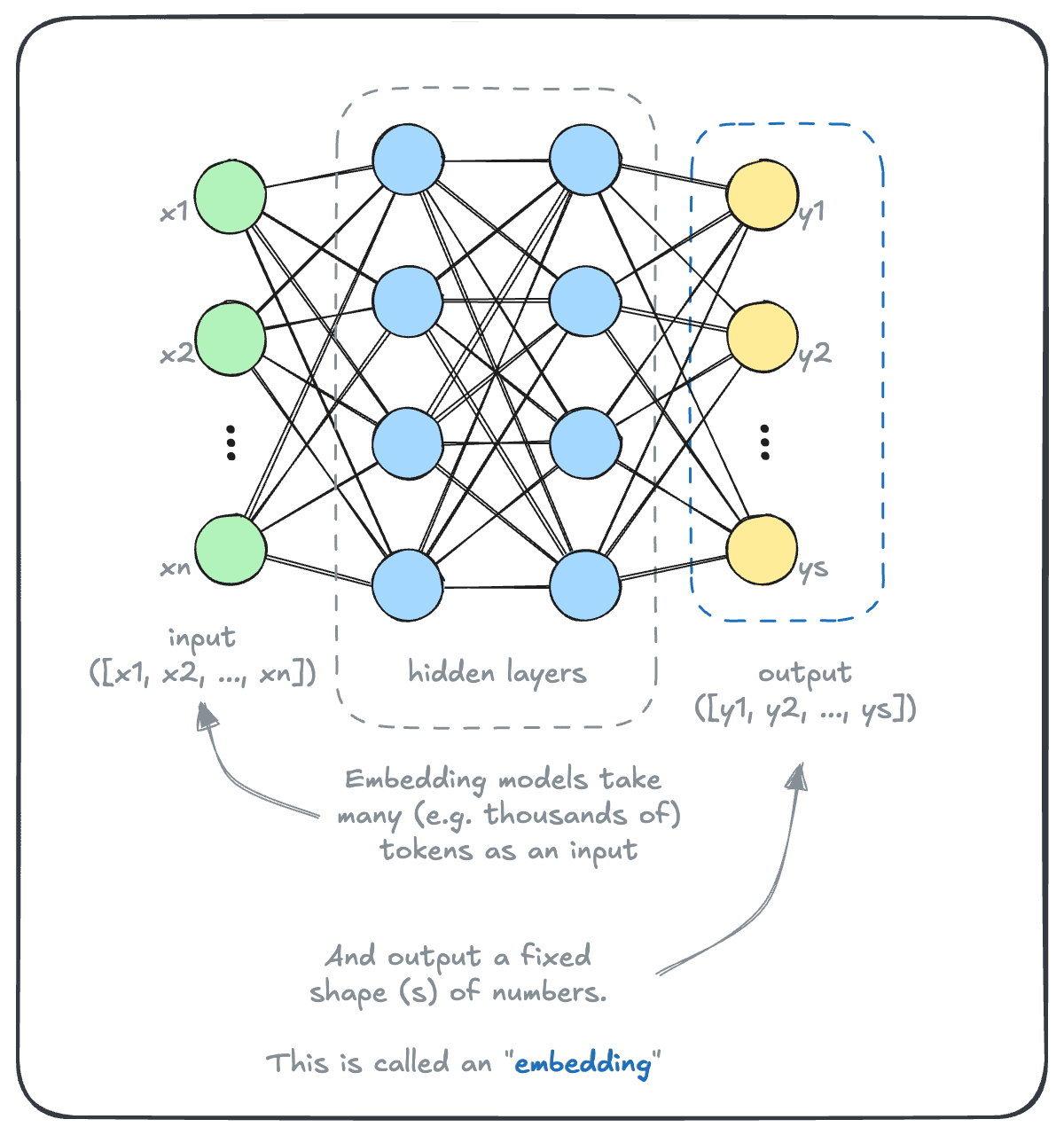
As you might imagine, this is not a trivial task. And there have been huge advancements in the field over the last decade or so. As an illustrative example, let’s take a look at the difference between the performance of two models at either end of that time scale.
An example evaluation
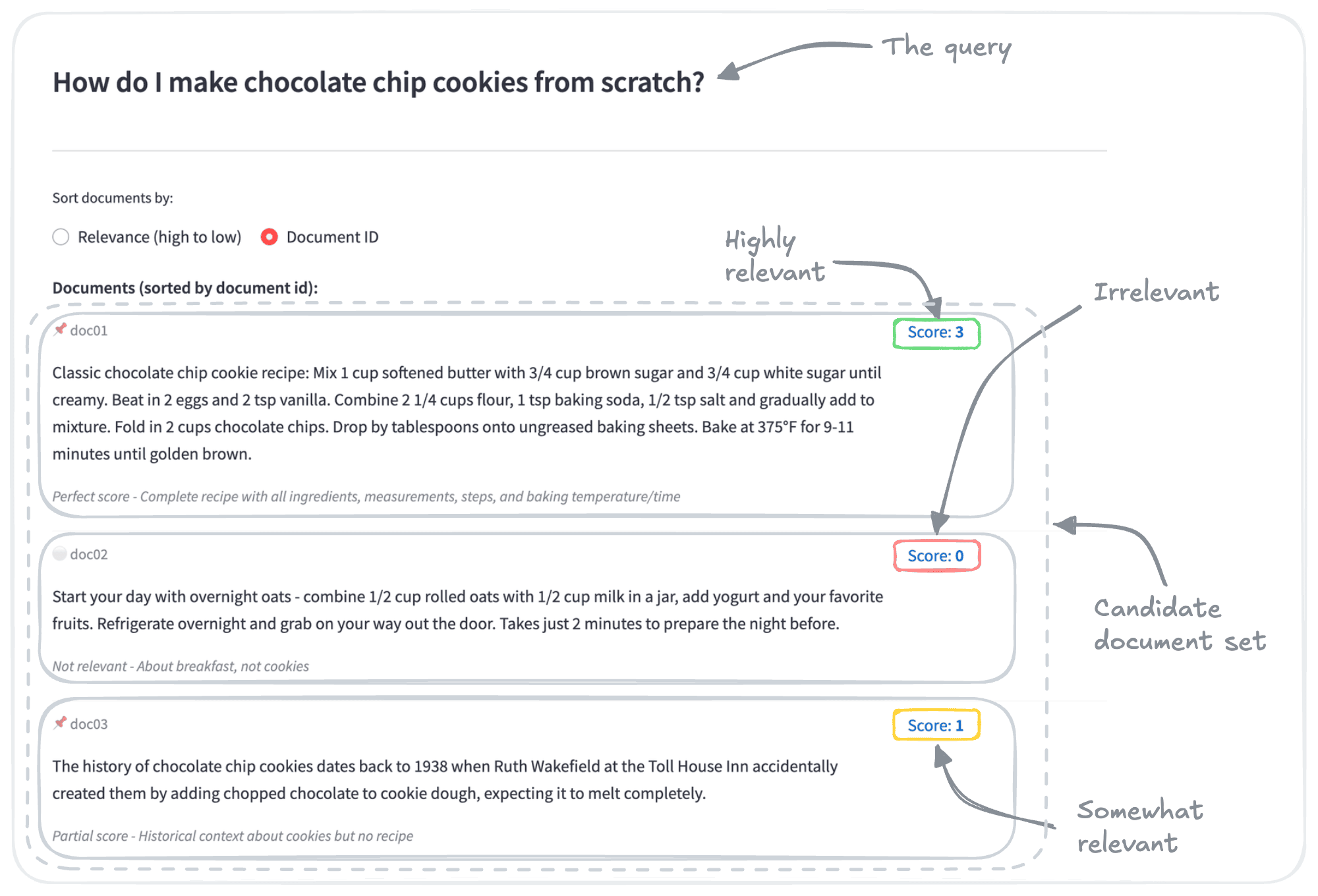
Here is a screenshot from an example demo application carrying out embedding evaluation.
In this example, we look for documents that best match the query “How do I make chocolate chip cookies from scratch”, out of a candidate document set of 20 documents.
Each of the 20 documents in the set has a “score” attribute here, where a more relevant object is indicated with a higher score.
Now, let’s see what happens when we try to retrieve the best matching objects using two different embedding models. We will use the following two models:
FastText (fasttext-en-vectors)(from 2015; model card)snowflake-arctic-embed-l-v2.0(from 2024; model card)
Here is a summary of results from a search, using the FastText model from 2015:
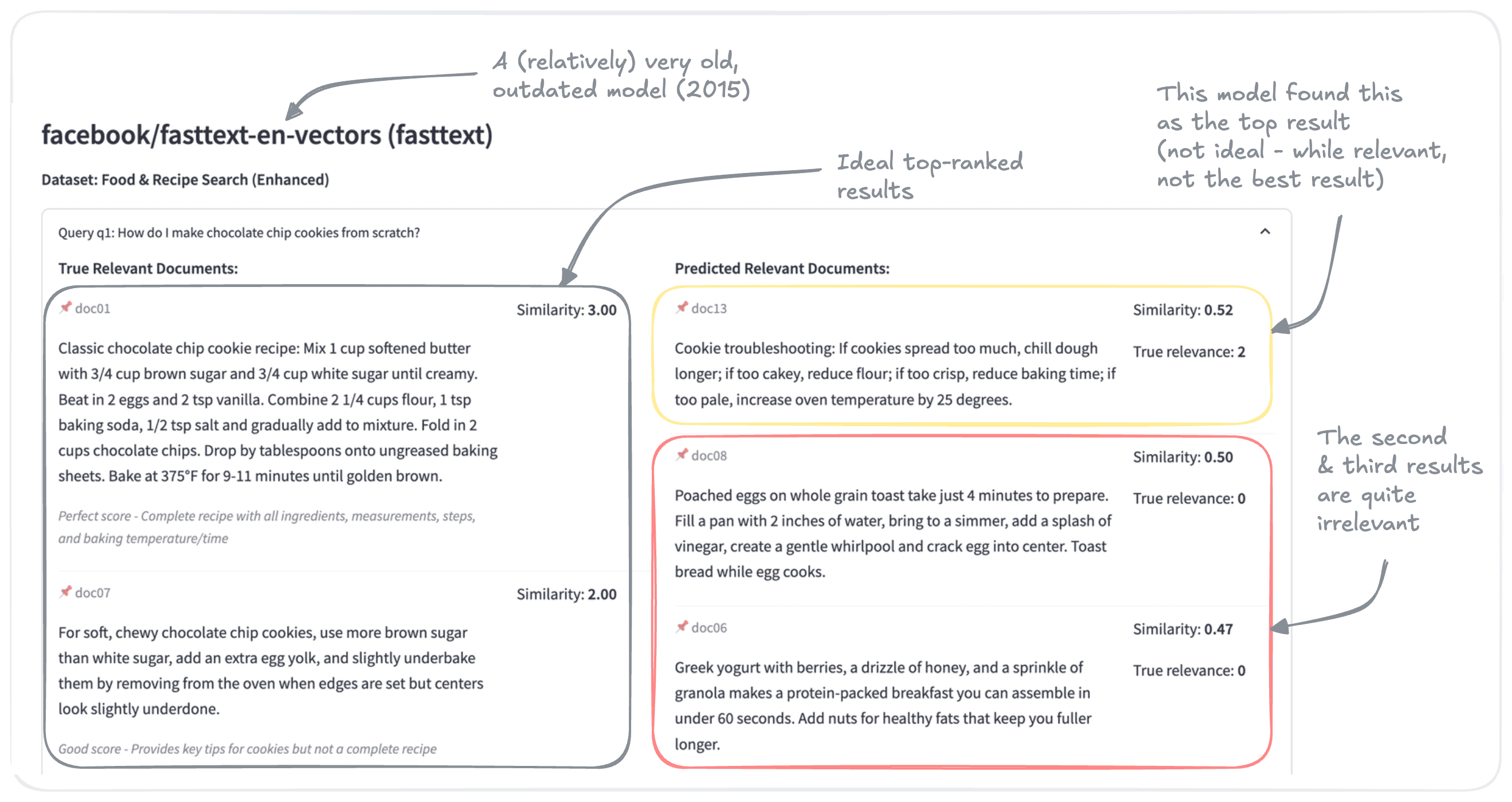
The top result identified by the FastText is quite relevant, as it discusses how to correct some potential issues with cookie making. However, it’s less relevant than the idea result, which is a step-by-step recipe.
The other two, however, are not relevant to the query. While they are recipes, they are not for baking cookies.
It would be fair to say that there’s quite a bit of room for improvement.
Here are the results from the snowflake-arctic-embed-l-v2.0 model, from 2025:
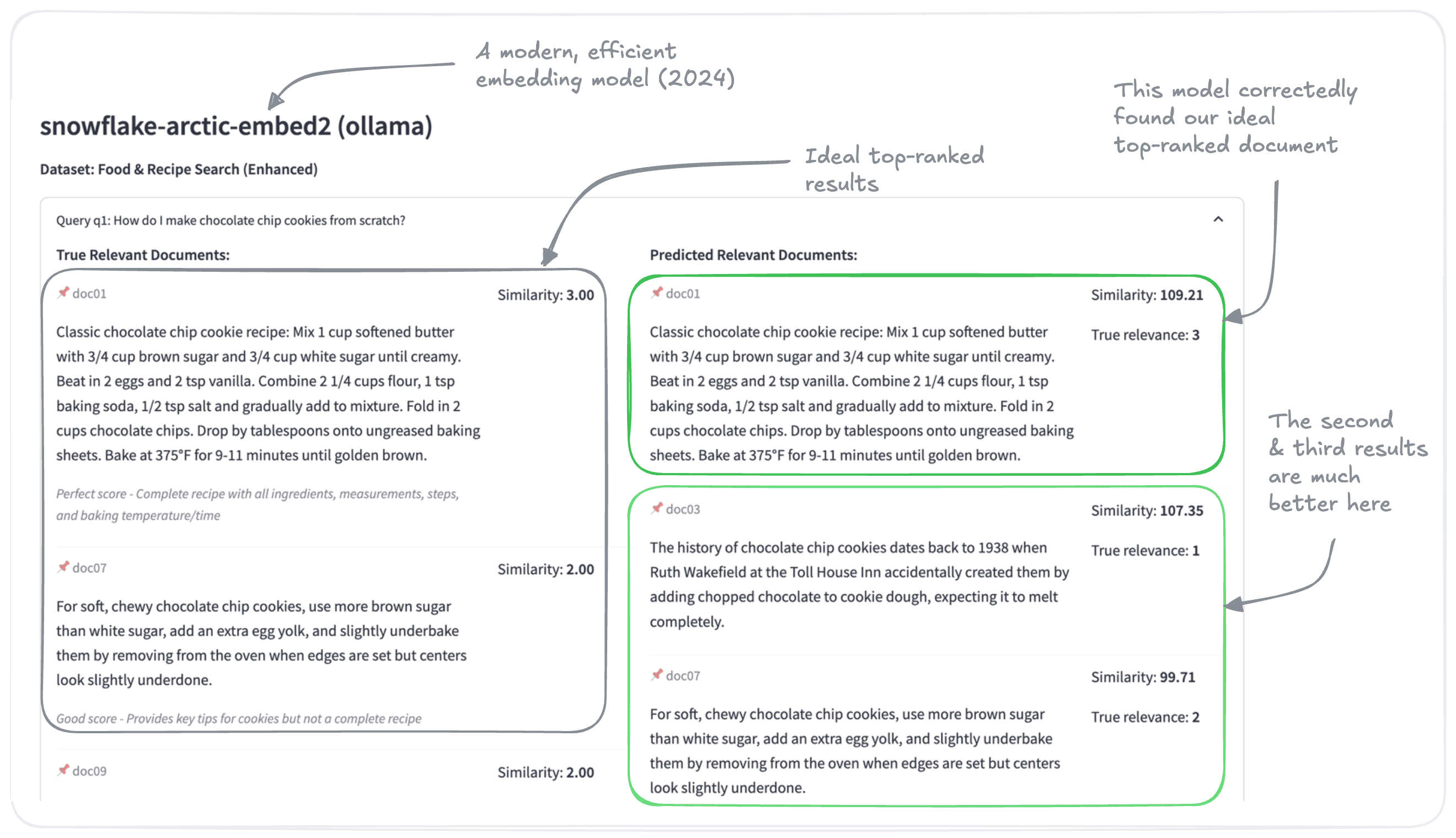
We see that the arctic embeddings correctly identified the ideal top-ranked result. In fact, the top two expected results are included in the top three results for the arctic embeddings. Even the other result is relevant to chocolate chip cookies - although perhaps slightly off topic.
Evaluation criteria
We could even compare these models using a standard metric, such as nDCG@k.
For this scenarios, the two models scored:
| Model | nDCG@10 |
|---|---|
FastText | 0.595 |
snowflake-arctic-embed-l-v2.0 | 0.908 |
What is nDCG@k?
nDCG is a metric used to evaluate the returned results in information retrieval. It rewards the model for returning the most relevant results at the top of the list. The @k indicates that only the top k results are considered.
The size of embeddings produced is another key factor.
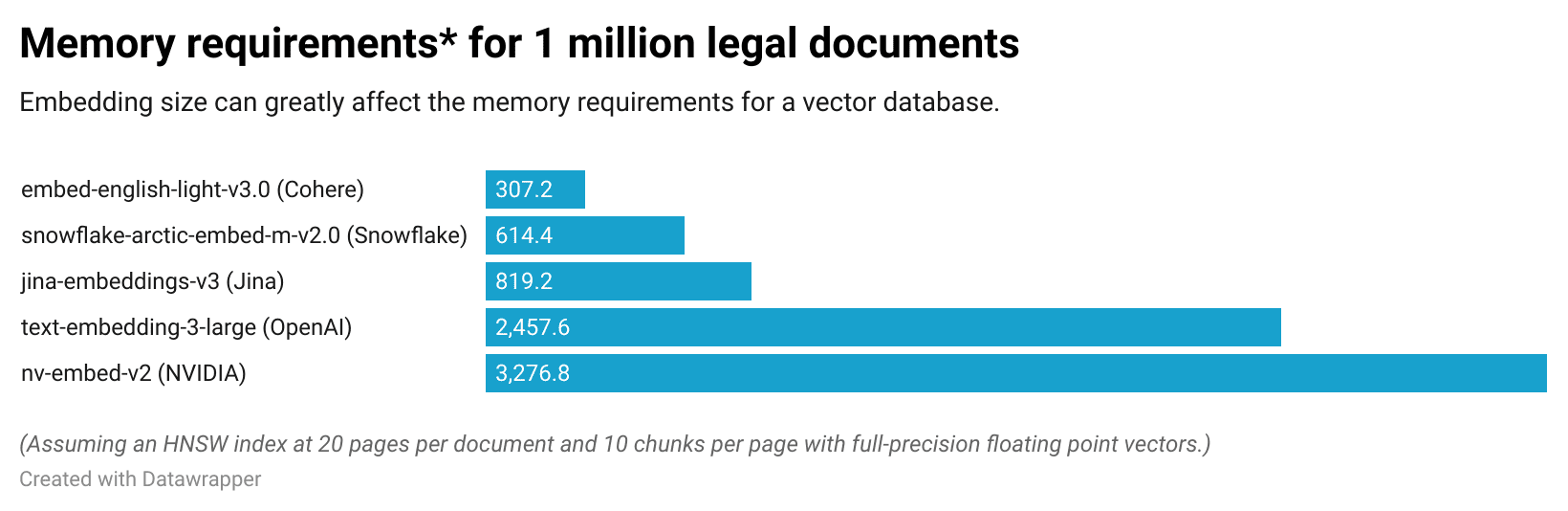
Embeddings can vary greatly in size, from around 300 dimensions to thousands. Imagine a service provider that hosts an AI bot that answers questions about legal cases. A vector database with 1 million documents*, one embedding model (nv-embed-v2) could require as much memory as 3.3 TB of memory, while another (embed-english-light-v3.0 ) might only require 300 GB of memory. (The following chart takes some popular models, and compares how each one would affect memory requirements.)
These simple examples illustrate some of the impact of embedding model selection. The choice of embedding models can make a huge difference in the quality of your search, your resource requirements, and many more factors.
There have been huge advancements in the landscape of embedding models over the last 10 to 15 years. In fact, innovations in embedding models continue to occur today. You might have heard of some of these names: word2vec, FastText, GloVe, BERT, CLIP, OpenAI ada, Cohere multi-lingual, Snowflake Arctic, ColBERT, and ColPali.
Each model (or architecture) brings with it some improvements. It may be in model architecture, training data, training methodology, modality, or efficiency, for instance.
So in the next few sections, let’s begin to explore a workflow for embedding model selection.
Questions and feedback
If you have any questions or feedback, let us know in the user forum.
